Question 4
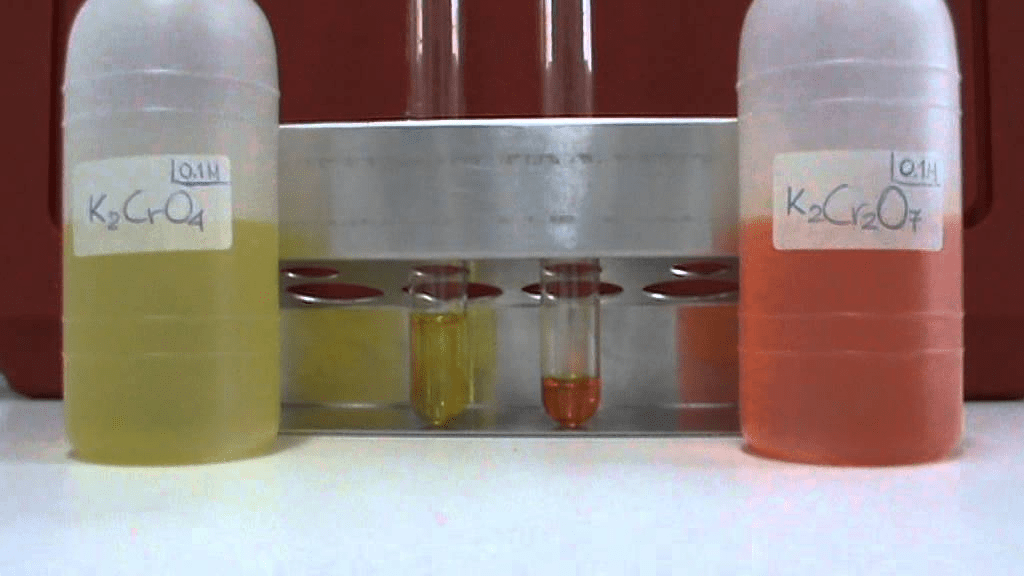
Potassium Chromate is a yellowish, crystalline compound.

Question 10
First Ionization Energy: He > Ne > Ar > Kr > Xe
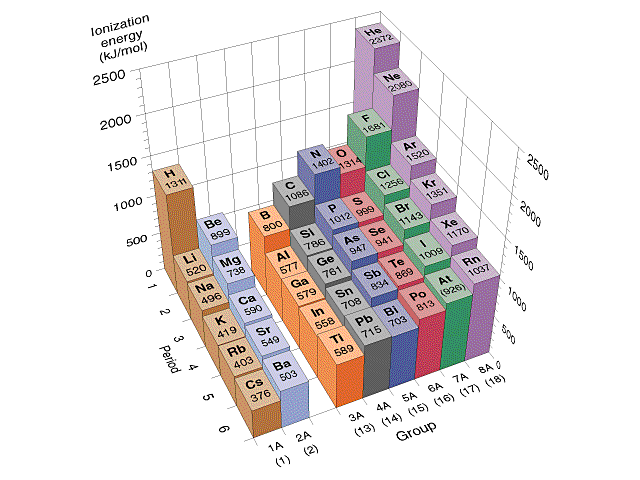
Question 15
A typical Lewis acid-base reaction:
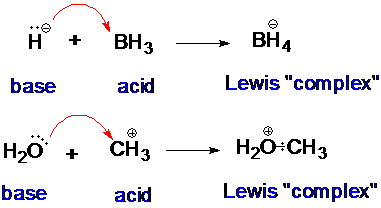
Question 23

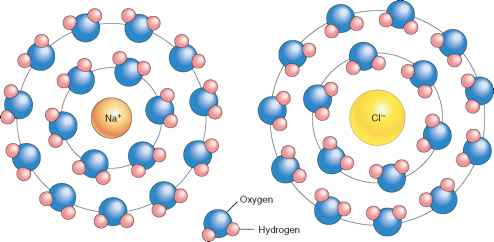
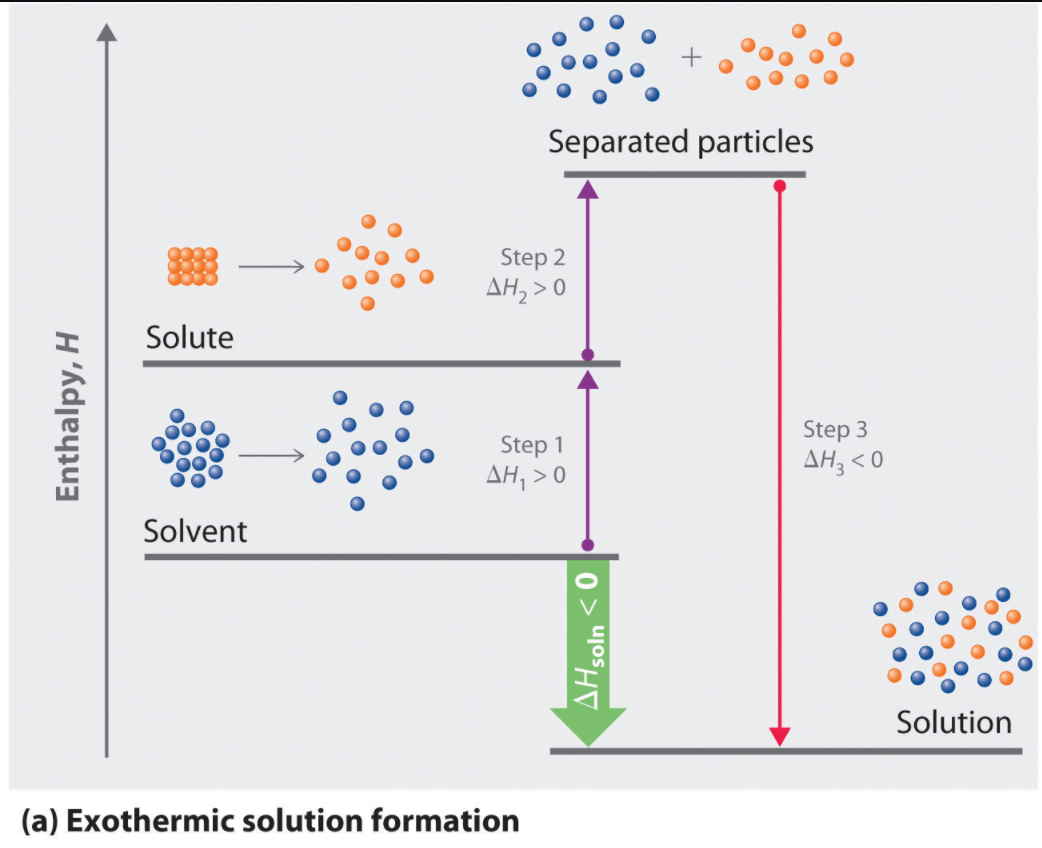
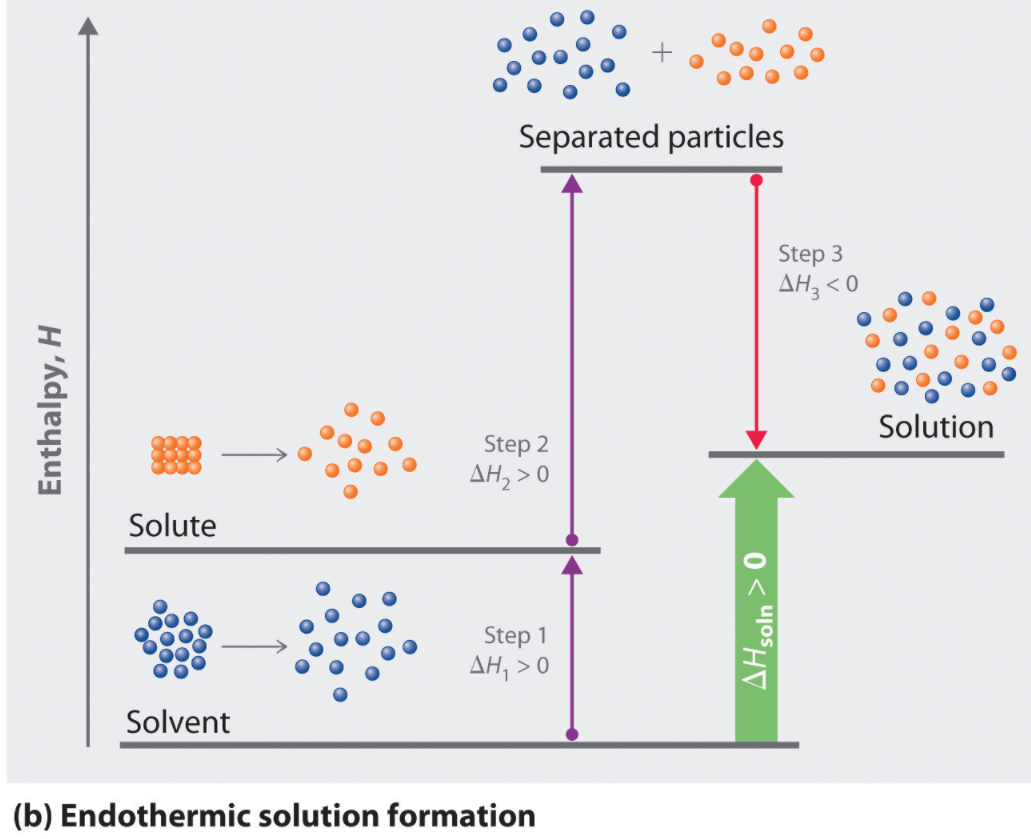
- For the process of solid calcium chloride dissolving in water, the entropy change is negative since water molecules in the hydration shells of Ca2+ and Cl- ions are more ordered than they are in the pure water
Question 28
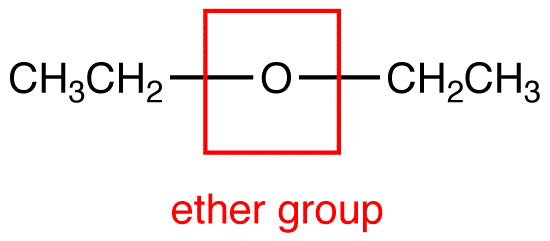
Question 30

Question 34
N2H4 exhibits significant hydrogen bonding in the liquid state.
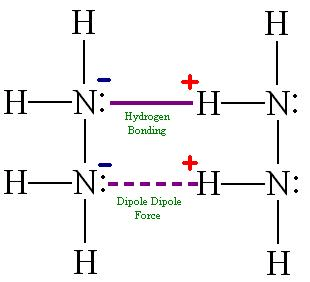
Question 37
Question 38
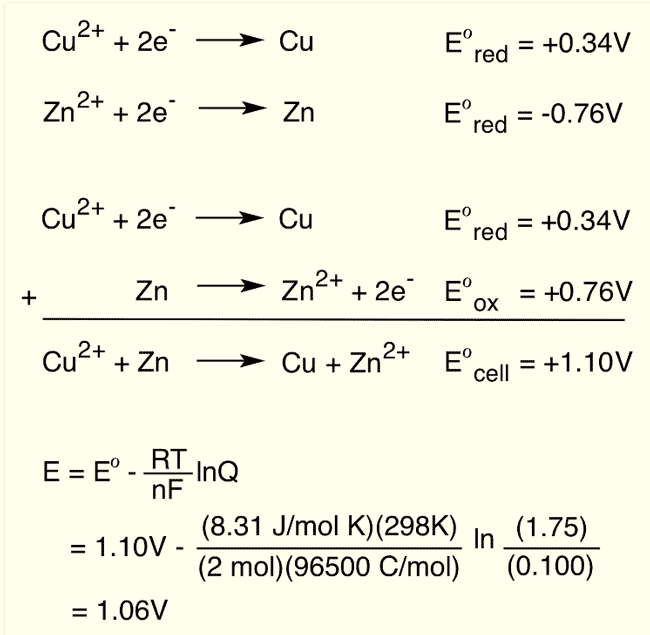
Calculate standard cell potential for the galvanic cell:
Question 40
Beta plus decay vs Beta minus decay
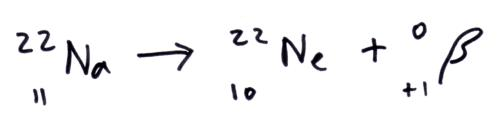
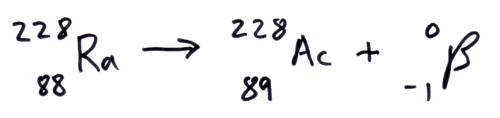
Question 47
![Zeroth Order First Order Second Order Differential rate law Concentration vs. time Integrated rate law Straight-line plot to determine rate constant Relative rate vs. concentration Half-life Units of k, rate constant Rate = o o o o ALA] At Time Slope = —k Time Rate — o o ALA] = MA] At Time o o —kt or Slope = —k Time [A], M Rate, M/S o o o o 2 3 M Rate, M/s 2k 2 3 Rate = 2 3 A[A] = At Time Slope = k Time Rate, M/S 4 9 2 3 0.693 l/s ](./media/image22.png)
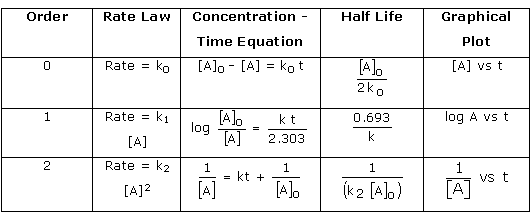
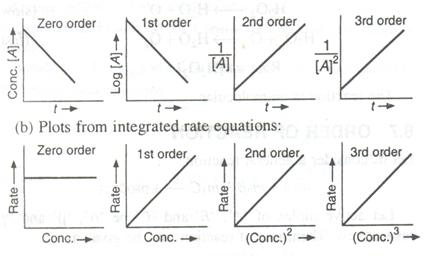
Question 51
O3 contains bonds that have a bond order of 1.5
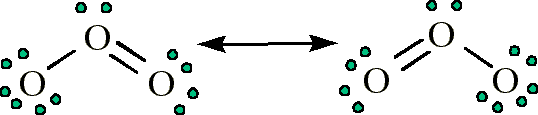
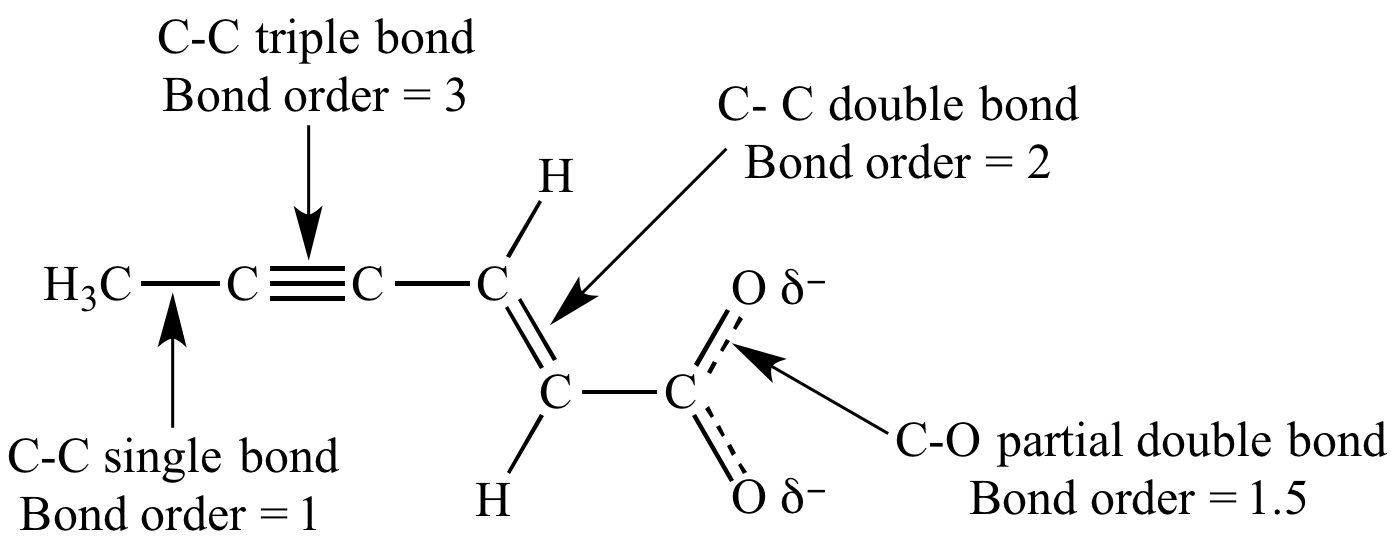
Question 67
Question 71
Endothermic: Separation of solute and solvent
Exothermic: Intermolecular attractions form between solute and solvent